Zunesis Honored on the 2021 Tech Elite 250 by CRN®
Tech Elite 250 List Honors the Highest-Achieving IT Solution Providers in Vendor Certifications
DENVER, CO, March 22, 2021
 Zunesis, announced today that CRN®, a brand of The Channel Company, will honor Zunesis on its 2021 Tech Elite 250 list. This annual list features IT solution providers of all sizes in North America that have earned cutting-edge technical certifications from leading technology suppliers. These companies have separated themselves from the pack as top solution providers, earning multiple, premier IT certifications, specializations, and partner program designations from industry-leading technology providers.
Zunesis, announced today that CRN®, a brand of The Channel Company, will honor Zunesis on its 2021 Tech Elite 250 list. This annual list features IT solution providers of all sizes in North America that have earned cutting-edge technical certifications from leading technology suppliers. These companies have separated themselves from the pack as top solution providers, earning multiple, premier IT certifications, specializations, and partner program designations from industry-leading technology providers.
Businesses rely on solution providers for an enormous amount of technologies, services, and expertise to help them meet today’s IT challenges — whether it’s a new implementation or digital transformation initiatives. To meet these demands, solution providers and MSPs must maintain high levels of training and certification from IT vendors and achieve the highest tiers within those vendors’ partner programs.
Each year, The Channel Company’s research group and CRN editors distinguish the most client-driven technical certifications in the North American IT channel. Solution providers that have earned these high honors — enabling them to deliver exclusive products, services, and customer support — are then selected from a pool of online applicants as well as from The Channel Company’s solution provider database.
Zunesis was founded in 2004 and for more than 16 years now, we have been focused on design, implementation, support and protection of our client’s IT Environments. Our team of IT Professionals average over 23 years of experience across all facets of the IT Infrastructure, including Compute, Storage, Backup/Recovery, Networking, Hyper-Visors, and Microsoft Server and Desktop. It is important that Zunesis stays on top of the latest technologies and implementations to service our customers.
“We are proud of the impact that Zunesis has had in the Rocky Mountain region with servicing our clients’ needs. ” commented Zunesis CEO, Steve Shaffer. ” “Since the beginning, we have believed that the client’s needs trump everything else and that making the lives of our clients better is a high and worthy calling.”
“CRN’s Tech Elite 250 list highlights the top solution providers in the IT channel with the most in-depth technical knowledge, expertise, and certifications for providing the best level of service for their customers,” said Blaine Raddon, CEO of The Channel Company. “These solution providers have continued to extend their talents and abilities across various technologies and IT practices, demonstrating their commitment to really conveying the most exceptional business value to their customers.”
Coverage of the Tech Elite 250 will be featured in the April issue of CRN® Magazine and online at www.CRN.com/techelite250.
About Zunesis
Zunesis, headquartered in Englewood, Colorado has been an HPE Platinum Partner for 16+ years. Zunesis has expert engineers in HPE server, storage and networking technologies along with common software applications like Veeam and Microsoft. Zunesis serves clients large and small but our sweet spot is the mid-market organization – the heartbeat of the US economy. Our mission is to make the lives of our clients and community better. www.zunesis.com
Follow Zunesis: Twitter, LinkedIn and Facebook
Zunesis Company Contact:
Rachael Stiedemann
Zunesis
rachael.stiedemann@zunesis.com
Data Protection
In the age of ransomware and digital transformation, your company’s data is even more critical than ever to keep your business running. While avoiding data loss is the main priority of backups, it can often be hard to balance that with the cost of those backups. On top of all that, data is harder to manage and control than ever due to multi-cloud infrastructure and workers more often working remotely.
So how do you deal with all of that and still have a trusted backup in case the worst should happen? You need a single, robust solution for data management that can protect your data through all phases of its lifecycle.
Veeam has been a leading player in the backup space for a while now. It has really stepped up when it comes to addressing new challenges in data protection. It has a host of different products, enterprise to consumer, that make it easy for businesses big and small to tackle the issue. They continue to innovate and keep your data secure while remaining flexible enough to fit into any environment. This year is no different with the release of Veeam version 11.
So what is new in the newest version of Veeam?
Continuous Data Protection, or CDP
It integrates with VMware environments to eliminate downtime and minimize data loss with a host of new features. CDP will eliminate the need for VM snapshots with I/O level tracking, and reduce the bandwidth needed for replication. It works on any OS or application as long as they are running in a vSphere VM. CDP will also schedule your jobs for you, just define the required RPO and CDP will take care of it. Depending on the amount of data, CDP can also offload data processing from your hosts to proxies. It calculates the required bandwidth to eliminate guesswork.
Hardened Repositories
This keeps your backups safe from malware and hackers with immutable backups. Single-use credentials are never stored in the configuration database eliminating any possibility of those credentials being extracted from a compromised backup server.
Expanded Object Storage Support
This feature reduces the cost of long-term archives. Veeam now integrates with Amazon S3 Glacier and Azure blob archive storage which are best for very long-term storage. These repositories can be made immutable, and are policy-based, so no management required.
Expanded Instant Recovery
It makes even more of your workloads instantly available. Instant recovery has been a feature of Veeam for a while, but now it has been expanded to include SQL and Oracle databases. Regardless of size, databases are made available to production applications and clients in minutes. You can then finalize those recoveries either manually, or by scheduling them to switch as soon as synchronization catches up, or even scheduling the switch during maintenance hours.
More Improvements
Veeam has made many more improvements with Version 11, enhancing many aspects of the program. GFS and Archive backups have added functionality. Powershell is now more powerful. Backup speeds have increased. Compliance with WORM backups has been added. As well, the GUI has seen some improvements. All of these features are included with normal licenses, you don’t need to pay extra for any of this stuff.
I am barely even scratching the surface on what is in the new version. I am most excited about the steps Veeam is taking to make their product more resilient against viruses and ransomware. Ransomware attacks have ramped up over the last few years. Keeping good copies of data in case of such an attack has been a struggle. Companies like Veeam have been in an arms race against hackers. Things like immutable backups are a huge leg up in the fight. Maybe someday, we won’t have to worry about that stuff, but for now, at least we have Veeam.
Contact Zunesis to find out more about Veeam V11.
Desire for IT Infrastructure Transformation
Over the past year, we have seen a substantial increase in the demand of organizations wanting to right-size, refresh, or otherwise transform their IT infrastructure/data center. Many organizations want to understand their opportunities to improve efficiency and service to the business and end-users through newer technology and IT delivery methodologies. Because the pressure to transform is increasing, many organizations are running head-first into change without clearly understanding the needs of the business or the most cost-effective strategy to deliver IT. One of the most common questions we hear from clients is “what workloads should I move to the cloud”? To effectively answer this question. a process of discovery and planning needs to be done.
IT Infrastructure Transformation Methodology
Over the past 16 years, our business (Zunesis) has developed a methodology and a group of talented technologists who work closely with clients to transform their IT infrastructure. First, we work to understand the business and the user requirements that matter today and tomorrow. We hear frequently from clients that they spend 90% of their time putting out fires and never find the time to develop a strategic IT infrastructure architecture, plan, or roadmap. The Zunesis IT infrastructure transformation methodology forces the production of these activities and documents. These delivery artifacts provide the guidance and direction for organizations to shape their IT infrastructure solutions now and into the future.
The Zunesis IT infrastructure transformation methodology prioritizes availability, resiliency, security, manageability, and performance. Our experience spans next-generation IT infrastructures for commercial and public sector organizations of all sizes and missions. The design efforts also take into consideration the financial constraints and the IT expertise of the organization.
We know transformation projects like this demand strong leadership and rigorous project management. We recognize that leadership and rigorous project management without outstanding communication are likely to cause problems. For this reason, our leadership approach is one of over-communication. We plan to keep all important stakeholders involved and engaged throughout the process. Zunesis provides supportive leadership in areas where presentations, justifications, logical explanations, and other communications are available to members of the leadership team.
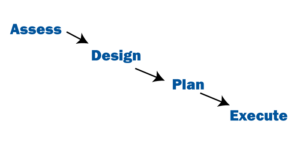
The Key Phases of our time-tested IT Infrastructure Transformation Methodology include:
- Assess
- Design
- Plan
- Execute
Assess
The Assessment phase sets the foundation for the rest of the engagement and requires a commitment of time from each of the key stakeholders in the organization. At Zunesis, we keep this process efficient by using a proven approach and seasoned and experienced IT professionals. We utilize efficient forums to collect, analyze and validate requirements and current infrastructure details.
Our approach includes reviewing existing documentation, workshops, on-line surveys, and interviews. This phase documents the current state of the IT infrastructure. This is all done with a consensus understanding of core business functions and desired future state of IT infrastructure requirements. During the Assessment Phase, it is also important to gain an understanding of any business or financial constraints as they will provide guard rails during the design and planning phases.
Design
During the Design phase, developing the technology framework occurs. This is a guide to prioritize IT initiatives and projects. This phase also stack ranks the key technology strategic initiatives for the organization. All of the data and requirements collected during the Assessment Phase are used to inform the development of the IT Framework. The Zunesis team then creates and documents the Framework process and procedures. The IT infrastructure Framework along with the selected IT initiatives (priority and order) are presented, discussed, revised, and finalized.
Plan
The Planning Phase is where we build robust plans to ensure the successful implementation/deployment of the prioritized IT infrastructure projects. Zunesis recommends the development of a Technology Deployment Roadmap / Plan to describe the prioritized projects and the timeline for the implementation of those projects. Given resource, financial, and business constraints, the Technology Deployment Roadmap may define a 12-month timeline up to a 60-month timeline. It is most common for a roadmap to be 2-3 years long.
For each infrastructure initiative defined during the design phase, the associated IT projects and objectives to achieve them are defined. The hardware, software, and personnel need to accomplish these projects are also clearly defined. A detailed plan is developed for each project. We review each project plan thoroughly with the client and validate against resource, timeline, and financial constraints.
Execute
The Execution phase involves the actual implementation of selected IT projects to meet strategic IT initiatives and priorities. The IT infrastructure Framework and Roadmap are guides that inform every step of the project. All of these architectural, strategic, and structural documents ensure consistency and predictability during the execution/deployment phase.
The Zunesis team produces a Portfolio Management methodology and strategy including an organizational structure and process for management of the project portfolio defined in the Planning Phase. Documents and templates are created to support the management and communication processes during the execution phase.
Zunesis provides clients with a time-proven and efficient methodology for the development of a next-generation IT infrastructure. Our staff of consultants and engineers make the process as simple as possible while ensuring thoroughness and professionalism. Please reach out to Zunesis to see how we can help you with your IT infrastructure
Network Access Control (NAC) – keeping the devices and users where they belong.
I work in a lot of network environments and I see a lot of different approaches to security and networking. One constant I have found is that all IT professionals struggle to adequately identify and secure the devices that may be on their network. Aside from having insane levels of security and prohibitive onboarding practices for devices, it is almost impossible to dynamically assign network access without the use of a network access control solution. I will dive into the basics with my mostly vendor agnostic explanation.
What a NAC is.
At the most fundamental level, network access control systems are designed to help identify devices and users on your network and then do something with the identification. The solution often integrates with most directory or identity providers. It can be used for authentication, authorization, and access. (AAA) The system can leverage hard-coded attributes of the user or device and enforce a security posture to them. The NAC can also leverage other components like how the device is connecting, where the devices are connecting from, and other more nuanced dynamic characteristics of the connectivity and identity.
What the system does with that information is the most important part. As an example, it is rare that every person in a business network should have the same access. However, it is not rare that many people in a department or division would have very comparable access or restrictions. Similarly, devices that are generally doing the same job likely require identical network access. If the NAC can leverage user attributes like department or division then it can use similar attributes for a device. It understands that an HVAC air handler requires the same access as was assigned to the other air handlers that share the same device attributes.
Enforcement Policies
With the use of what some vendors call roles with enforcement policies, one can automate the application of access based on identity. This allows for a scalable solution that can deliver the same application of security without the intervention of an administrator for every network connection. This concept is called role-based access.
I use the term application of security very loosely because each vendor accomplishes this task in different ways. Some will tunnel the user traffic to a firewall or wireless controller and apply stateful firewall policies to the user traffic. Others will change the network or VLAN the device is on so that the access is restricted to that network segment. Some rely on client-side software to enforce the application of a role assigned from the NAC.
Other helpful things a NAC can do
- Integrate with endpoint AV software to assess the vulnerability of a client and use that as an attribute for access.
- Apply the same security posture to both wired and wireless clients.
- Centralize the administration and logging for all AAA exchanges.
- Integrate with edge firewalls from Cisco, Palo Alto, Fortinet, and others
What a NAC is not
A network access control solution is not the panacea that will make all your aliments cease. NACs by themselves hold a great deal of machine learning potential. It does require some semblance of initial administration to create the logic by which they will apply the enforcement of policies from. They are not infallible. Like any computing system, they do need some TLC when first deployed. Once they are up and running, you can sleep easier at night knowing that there is an intelligent application of security for anything connecting to your network.
Here are a few other things they cannot do
- NACs are not meant for IP address management. I see a lot of people trying to use them as this and most are ill-suited for the task. Just because it has a record of the IP address does not mean it should be used as a database.
- They are not plug and play. No matter what the vendor tells you it will be a very involved deployment.
- Not every NAC integrates with every other product. Each vendor has their own special sauce that makes using their NAC with their equipment more appealing. Cisco, Aruba, FortiNet all have features that are only available when you are using their equipment with their NAC.
Use Cases
I would recommend a NAC to anyone who runs a network with more than 100 users. If we assume that each person will likely have three computing devices, then that is 300 end-user devices. Not all of them being corporate-owned and managed, we would need to delineate access for each user group and device type. We will then need to ascertain if we want to apply different security based on how the device/user connects or if the device presents a risk to the company. This sounds like a lot of work and it can be. But, the work would only need to be done one time if we were programming logic into a NAC solution.
Best application of NACs
- Securing wired ports – We all know that users will bring in devices from home to use so why not protect your environment from the inevitable.
- Wireless for everybody – Just because the device is connected to the same SSID as all the other devices, it does not have to mean that they have the same security applied or are on the same logical network.
- Dynamic logins for your most sensitive devices – Securing your switches, routers, and firewalls with Radius or TACACS+ is how you protect against getting hacked from the inside.
This is not meant as a comprehensive analysis of each of the major players in the marketplace. In fact, there are some decent open source and free NAC-like products out there that are relatively capable. Most of those do not support machine learning and cannot identify devices very well. However, they can provide authentication and authorization functions.
At the very least my hope was to impress upon anyone in the market that a NAC is a very necessary and essential component to your security arsenal. The days of having the same login for every switch and router are long behind us. Treating every user and device the same is also a thing of the past. If you desire the scalability that a network access solution provides, I suggest you reach out to your partner of choice. Inquire about what products they offer in this security space. Zunesis is available to help you find the right partner for your organization.
Decisions, Decisions, Decisions
When making the decision on what is the best solution for your infrastructure, there are a few popular options available. Options include Converged, Hyperconverged, and Disaggregated Hyperconverged. Depending on the size and complexity of your environment, this will impact which infrastructure you may choose.
Choosing between the different available architectures means having a complex understanding of both the current deployments in your data center and the scaling factors impacting your organization specifically.
Converged Infrastructure
IT Sprawl is still a very real issue for data centers. It leads to increased costs, reduced efficiency, and less flexibility. A converged infrastructure (CI) helps with this by creating a virtualized resource hub. It increases overall efficiencies across the data center using a single integrated IT management system.
A converged infrastructure (CI) aims to optimize by grouping multiple components into a single system. Servers, networks, and storage are placed on a single rack. Replacing the old silos of hardware, convergence allows IT to become more efficient by sharing resources and simplifying system management. This efficiency helps keep costs down and systems running smoothly. On the flip side, it is expensive and not the most flexible in scaling.
While converged infrastructure is effective in small-scale environments, most mid-market and enterprise organizations are limited by this architecture. Its hardware is proprietary in nature and it ineffectively distributes resources at scale.
Hyperconverged Infrastructure
Hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) was designed to fix the scalability issue, and it certainly improved things. Designed as a building-block approach, HCI allows IT departments to add in the nodes (i.e., servers, storage, or computing) as needed. It continues to simplify management by placing all controls under a single user interface.
Hyperconverged infrastructure, by leveraging commodity products across the board, significantly disrupted the financial dynamics. It was radically less expensive, at least initially than converged infrastructure while still providing most of the benefits.
Most organizations today use either a traditional CI or HCI Deployment. There are benefits and advantages to both.
While HCI has many benefits, there are some significant disadvantages. For quickly growing businesses that need an easy-to-manage architecture that embeds as many elements of modern-day computing – like disaster recovery, security, and cloud, this may not be the best solution. Hyperconverged solutions have use cases where they do not fit. This has caused problems for customers who disrupted operations by not realizing the impact some workloads would have.
While more scalable than CI, HCI still requires the interdependent growth of storage and servers. That’s a challenge with the types of workloads companies use today.
It’s hard to argue with the manageability and scalability advantages of traditional HCI platforms. IDC predicts that the HCI market revenue will grow at a CAGR of 25.2% to crest $11.4 billion in 2022. As HCI has matured, enterprises have been looking to use it to host a broader set of workloads.
There are still workloads whose performance, availability, and/or capacity demands encourage the use of an architecture that allows IT managers to scale compute and storage resources independently. A storage solution that is better for workloads whose growth is very dynamic and unpredictable.
Disaggregated HyperConverged (dHCI)
Enter in the latest solution, Disaggregated Hyperconverged infrastructure. Disaggregated hyperconverged infrastructure (dHCI) combines the simplicity of CI and the speed of HCI to create a more resilient, evolved data center architecture. There are numerous benefits to dHCI. The biggest value proposition most attractive to users today is disaster recovery as a service or DRaaS.
While not every workflow can run on a hyperconverged infrastructure, they can on a dHCI. That’s part of what makes it appealing. It doesn’t come with the restrictions of its predecessors. Ultimately, disaggregated HCI leverages similar components to converged infrastructure but leverages modern infrastructure automation techniques to enable automated, wizard-based deployment and simple, unified management at similar costs to HCI.
With dHCI, IT teams are able to focus on support and service delivery while Artificial Intelligence (AI) takes care of infrastructure management. The rise in size and complexity of data centers means that such an intelligent solution will help firms get maximum Returns on Investment (RoI) in IT equipment.
dHCI is in demand for IT managers who want the simplicity of HCI and the flexibility of converged. dHCI is simple to deploy, manage, scale and support. It is software-defined so compute and storage are condensed and managed through vCenter with full-stack intelligence from storage to VMs and policy-based automation for virtual environments are integrated throughout.
HPE Nimble Storage dHCI
HPE Nimble Storage dHCI pulls together the best elements of each type of infrastructure. Combining the simplicity of HCI management with the reliability, familiarity, and flexibility of scale of our beloved 3-tier architecture. It is essentially high-performance HPE Nimble Storage, FlexFabric SAN switches and Proliant servers converged together into a stack. Simple deployment, operation, and day-to-day management tasks have been hugely simplified with this solution.
The out-of-box experience requires very little technical experience to use and deploy the stack. Once up and running, day-to-day tasks, such as adding more hosts or provisioning more storage, are simple “one-click” processes that are simple and take up very little technician time. Storage, compute and networking can be scaled independently of each other. This further reduces the requirement for VMware/ Hyper-V licensing at scale. It reduces the costs as there isn’t a need to scale out all the components when you simply need more storage or compute.
The whole stack plugs directly into the HPE Infosight portal and support model. It automates simple support tasks so that 1st and 2nd line support are no longer needed to triage issues. dHCI plugs into this to bring this first-class support and analytics to VMware, Proliant, and FlexFabric as well as the Nimble Storage platform. With dHCI, it’s now possible to deploy an entire virtualization stack and have it monitored and supported 24/7/365 by skilled HPE engineers.
Want to learn more about these infrastructure solutions and discover which one is a good fit for your organization, request a consultation today with Zunesis.
Do your Linux servers use LVM?
If not, you should strongly consider it. Unless, you are using ZFS, BTRFS, or other “controversial” filesystems. ZFS and BTRFS are outside of scope for this discussion but are definitely worth reviewing if you haven’t heard of them and are running Linux in your environment.
Logical Volume Manager for Linux is a proven storage technology created in 1998. It offers layers of abstraction between your storage devices in your Linux system and the filesystems that live on them. Why would you want to add an extra layer between your servers and their storage you might ask?
Here are some reasons:
- Flexibility
- You can add more physical storage devices if needed, and present them as a single filesystem.
-
Online maintenance – Need to grow or shrink your filesystems, online, and in real-time? This is possible with LVM.
-
It is possible to live migrate your data to new storage.
- Thin provisioning can be done, which can allow you to over-commit your storage if you really want to.
- Device naming – you can name your devices something that makes sense instead of whatever name Linux gives the device.
- Meaningful device names like Data, App, or DB are easier to understand than SDA, SDB, SDC
- This also has the benefit of reducing mistakes when working with block devices directly.
- Performance – it is possible to stripe your disks and improve performance.
- Redundancy – it is also possible to add fault tolerance to ensure data availability.
- Snapshots
- This is one of my favorite reasons for using LVM.
- You can take point-in-time snapshots of your system
- Those snapshots can then be copied off somewhere else.
- It is also possible to mount the snapshots and manipulate the data more granularly.
- Want to do something risky on your system, and if it doesn’t work out, have a quick rollback path? LVM is perfect for this.
So how does it work?
According to Red Hat :
“Logical Volume Management (LVM) presents a simple logical view of underlying physical storage space, such as hard drives or LUNs. Partitions on physical storage are represented as physical volumes that can be grouped together into volume groups. Each volume group can be divided into multiple logical volumes, each of which is analogous to a standard disk partition. Therefore, LVM logical volumes function as partitions that can span multiple physical disks.”
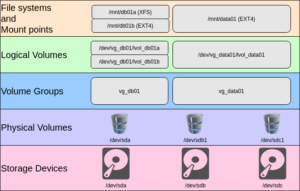
I think LVM is much easier to understand with a diagram. The above image illustrates some of the concepts involved with LVM. Physical storage devices recognized by the system can be presented as PVs (Physical Volumes). These PVs can either be the entire raw disk, or partitions, as illustrated above. A VG (Volume Group) is composed of one or more PVs. This is a storage pool, and it is possible to expand it by adding more PVs. It is even possible to mix and match storage technologies within a VG. The VG can then allocate LVs (Logical Volumes) from the pool of storage, which is seen as raw devices. These devices would then get formatted with the file system of your choice. They can grow or shrink as needed, so long as space is available in either direction for the operation.
You really should be using LVM on your Linux servers.
Without LVM, many of these operations discussed above are typically offline, risky, and painful. These all amount to downtime, which we in IT like to avoid. While some may argue that the additional abstractions add unnecessary complexity, I would argue that LVM really isn’t that complicated once you get to know it. The value of using LVM greatly outweighs the complexity in my opinion.
The value proposition is even greater when using LVM on physical Linux nodes using local storage. SAN storage and virtual environments in hypervisors typically have snapshot capabilities built-in, but even those do not offer all of the benefits of LVM. It also offers another layer of protection in those instances. Alternatively, the aforementioned ZFS and BTRFS are possible alternatives, and arguably better choices depending on who you ask. However, due to the licensing (ZFS) and potential stability (BTRFS) issues, careful consideration is needed with those technologies. Perhaps those considerations are topics for a future blog…
Want to learn more? Please reach out, we’re here to help.
Centrally Manage Your Maintenance Contracts
Maintenance contracts are supposed to deliver peace of mind. Yet, when you have dozens of contracts with various vendors – all with different renewal dates, they can quickly become a headache. We work with our customers to identify what hardware, users, vendors, and services are covered, as well as those that aren’t. With this information, we put together a plan to ensure your business is protected from unexpected downtime while saving you money on unnecessary support costs.
Each year, maintenance costs swallow 15% to 25% of total enterprise IT budgets. IT staff must constantly reduce and control these expenses. This is where we can assist you with doing a full evaluation of your maintenance contracts and advise you on the most cost-effective way of getting the coverage you need to keep your business protected. This enables IT staff to contribute strategically and allocates resources toward innovation and business initiatives, and away from day-to-day maintenance.
Ways to Help You Save Time and Money
HPE Hardware Maintenance Audit Process:
- Work with customer to identify Asset Inventory starting with HPE Asset Report (CAP)
- Collaborate with customer and HPE to gather any missing information
- Identify what services/deliverables are required to meet customer expectations
- Work to consolidate multiple support agreements via co-terming or combining contracts. This makes your renewals less frequent and allows for simplified budgeting.
- Terminate retired products and licensing – This eliminates wasted money for products that are no longer in production.
Software Maintenance Audit Process
A complete audit of your organization’s 3rd party licensing may show licenses are allocated to users who no longer require the application to perform their duties. Or, your business requirements have shifted, and you may need more functionality in your existing platform. Whatever the situation, Zunesis can assist in identifying those needs and:
- Work with the vendor to identify licensing entitlement, support expiration dates and service levels
- Evaluate real usage and compare license utilization to entitlements
- Negotiate a more cost-effective solution for your organization
- Recommend alternative solutions to reach your business goals and objectives
In addition to hardware and software support management, we offer a full portfolio of IT services to ensure you are on track to meet your 2021 business objectives. Our IT assessment services can provide you with the information you need to make informed decisions on your cloud strategy, infrastructure, and much more.
IT Assessment Services:
Our IT Health Check Services compare your infrastructure design to best practices and support levels. From there, we make recommendations to improve service levels and offerings.
- Reduce risk of downtime and lost productivity
- Protect against ransomware and viruses
- Work with a dedicated team of experienced IT professionals with a proven track record in managing industry-leading IT solutions.
IT Health Check:
- An IT health check represents an essential way of evaluating your business’ inner IT workings to ensure that there are no security breaches or potential problems
- Review and document your current IT environment, review current support requirements, and make recommendations for changes and updates according to best practices and supportability.
Migration Services:
Our Migration Services will bring our expertise and experience to make sure your risk is minimized and the project goes as smoothly as possible.
- Dedicated Support Team with industry certifications and expertise
- Dedicated Project Manager to keep your migration on schedule and keep you informed via planning, tracking, reporting, and accountability for your most important projects.
Installation Services:
Our IT Installation Services ensure that your technologies are implemented efficiently and effectively—the first time.
- Our comprehensive installation capabilities include servers, storage, networking, security, cloud, and backup and disaster recovery solutions.
- We have the knowledge, experience, and certifications to install and implement nearly every solution we sell.
As with any initiative, a well-defined strategy and a coordinated approach are critical. This helps to implement an effective maintenance cost reduction initiative that compliments your IT objectives.
Managing support warranties, licensing, and IT infrastructure can be overwhelming. Zunesis offers complete solutions in helping clients manage their IT infrastructure and warranties to avoid a gap in service. We provide the assurance that you are covered in case of an unexpected outage.
If you would like assistance in managing your multi-vendor support agreements, or to discuss solutions to ensure you have the most effective IT plan in place, please reach out to schedule a time to discuss how Zunesis can help your organization get your maintenance and infrastructure under control.
Santa made a list and he checked it twice. Let’s find out who’s naughty and who’s nice!
Naughty List
Who is on the naughty list this year?
-
- Ransomware Attackers
- Bad Password Creators
- Uncommitted Remote Workers
Wondering why Ransomware Attackers take the number one spot on this year’s naughty list?
Ransomware is malicious software that poses a threat usually by denying you access to your data. The attacker demands a ransom from the victim, with the promise to restore access to their data upon payment (which rarely happens even if the victim pays the ransom).
In 2021, the estimate is that a ransomware attack will take place every 11 seconds. The total damage could reach $20 billion. To break that out, in 2019 the average cost per ransomware attack was $133,000. Imagine a 90% chance of someone holding a $133,000 ransom over you. This is happening all too often, and it is happening in the world of technology. No, thank you…. “SANTA”! (tattletale voice).
Though not in the same league as a ransomware attacker, bad password creators and uncommitted remote workers take second and third place on Santa’s list of naughtiness.
Passwords
Passwords provide the first line of defense against unauthorized access to your computer and personal (and your company’s) information. The stronger your password, the more protected your computer will be from the hackers and malicious attackers mentioned above. One of the most common ways that hackers break into computers is by guessing passwords.
Simple and commonly used passwords enable intruders to easily gain access and control of a computing device. If you want to be considered the ‘good’ worker that you are and to receive ALL of the toys and treats that you deserve this year, it is imperative you put thought into creating a unique and somewhat complex password. This not only protects you from having your personal information compromised, but your company will thank you too!
Casual Remote Workers
Casual remote workers, or in other words, remote workers who do not take company policies and procedures seriously, are the last of the naughties. With so many people now working from home, assailants have more opportunity to pull off an attack. There is a myriad of ways in which a remote worker can lessen the chances of a company being compromised; the below is a good place to start:
1. Brute force attack through the VPN
In a brute force attack, a hacker uses a rapid trial and error approach to guess the correct password, PIN, or encryption keys. It doesn’t require a lot of intellect or complex algorithms – it’s merely a guessing game. (Refer back to #2 on the list – create unique passwords!)
2.Command and Control via Phishing
Phishing is the fraudulent attempt to obtain sensitive information or data, such as usernames, passwords and credit card details, by disguising oneself as a trustworthy entity in an electronic communication. (Take the time to really think about what you are being asked. Work with your IT team to learn how to identify a phishing email)
3.Bypass of Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication is an electronic authentication method in which a computer user is granted access to a website or application only after successfully presenting two or more pieces of evidence to an authentication mechanism. (When you are asked if you would like to set up multifactor authentication, the answer is always yes 😊)
Nice List
Who is on the nice list this year?
- SysAdmins/IT Departments
- IT leadership for navigating 2020
- Leaders who allocated budget to team members over products
SysAdmins
In a simple definition, System Administrators fix computer server problems; they organize, install, and support an organization’s computer systems. This includes local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), network segments, intranets, and other data communication systems.
In a more accurate description of SysAdmins and your IT Department; they are super(wo)men! These individuals have always been deserving of appreciation from the surrounding departments and people in their lives, but 2020 has challenged the company’s IT departments to deliver even more, even faster. Expectations are that they continue making your company’s communication working seamlessly. In today’s world, they work tirelessly to ensure remote workers are set up to be efficient. They work hard to implement, teach, and manage policies and best practices for remote workers. Not only is your IT department on the nice list this year, but they also get to eat the cookie dough from the Christmas Cookie bowl too! Score!
IT Leadership
IT leadership is another group that made the nice list. When no one knows what is going on (and I do mean no one), people look to leadership for guidance and direction. The difficulties of leading a group of people and an organization have their own challenges in a “normal” year but when you’re working from a recipe that encompasses budget cuts, the need for innovation, navigating new working situations, and the increased pressure of diminishing cyberattacks, a “successful” outcome can be hard to measure.
The following challenges were top on the list for IT leadership this year:
- Cybersecurity
- Digital transformation
- Cloud computing
- Hiring
- Budget
Increased pressure to perform with drastically lower budgets has forced IT leaders to identify their very top priorities in order to allocate budgets appropriately. Nothing new here, leaders have done this since the beginning of time, but when you think your budget is one thing and it QUICKLY becomes another, this balancing act isn’t nearly as easy as it seems. To the leaders who opted to take care of their employees over buying the latest and greatest; thank you!! Your team noticed and MOST IMPORTANTLY, Santa noticed! You know what they say, “he knows if you’ve been bad or good so be good for goodness sake!!”
Happy Holidays to you and yours!
Blogs typically are not hard to write. The trick is to find something relevant for the readers and something that is passionate to you. Just take a look at some of the blogs my teammates here at Zunesis have written.
The year 2020 and how the Covid-19 pandemic are affecting our world, a topic which is dominating every news cycle, no matter the industry:
2021 – It’s Only a Date Change – Peter Knoblock
Going Back to Basics – Tom Savage
2021 Strikes Back – Caleb Clark
CARES Act Funding to Assist with Distance Learning – Sara Wessells
Another Zunesis blogger, a fitness enthusiast, compared IT Health Checks and Assessments to doing Yoga.
Yoga + IT Health = Nirvana – Stacy Lara
These blogs were easy for the authors to write because they are passionate about their topics, our world, the industry we serve, and the customers we serve.
AD Health Checks
Over four years ago in May 2016, I wrote a blog titled: Why You Need to Check the Health of Your Active Directory.
First, I cannot believe that was four years ago, and second, it is still very relevant today. In fact, I would say more relevant, enough to expand the AD Health Checks to the entire server infrastructure.
In that blog, I compared Active Directory to the central nervous system of the human body. How, just as you see a doctor for regular checkups, AD also needs these types of checkups. If AD is the central nervous system, then the servers which support the infrastructure are the major organs. Just like the AD Health Check, the servers must be checked periodically.
Screen for Diseases
1. Verify backup solution: Be sure your backups are working. Daily reports need to be reviewed for completion and to identify issues. Perform test recoveries to be sure the backup solution is working at 100%. Don’t have a backup or unsure about your current solution? Zunesis has a blog for that:
Are You Sure You Can Recover Your Backups? – James Hughes
Protecting your Data with Veeam Backup – Adam Gosselin
2. Monitor Disk Usage: Servers generate a lot of data which can add up over time. Make sure you are getting rid of old log files. If they are needed, then archive them to permanent storage. Remove old applications that can leave significant security holes. Review the removal as some uninstallers can leave old files. A smaller data footprint means faster recovery.
3. Monitor system alarms for hardware: Check for any type of hardware warnings, errors, or failures. Warnings tend to lead to errors, which can lead to failures.
4. Monitor server resource utilization: Monitor disk, CPU, RAM, network utilization, and log files. Check for OS or Application issues.
5. Updates, updates, updates: Check for Operating System updates. Check for Application updates. Check for Hardware (Firmware) updates. Hackers are very quick and can develop variants within hours of an issue being disclosed. Rapid response is key.
6. Review privileged user accounts: Validate for accuracy and check account permissions to make sure they are appropriate for each user.
7. Review Password Security: User passwords should be changed every 45-60 days. Service Account passwords should be changed annually.
Future Health Precautions
Assess Risk of Future Medical Problems
- Review Microsoft Server Roadmap for planning migrations.
Encourage a Healthy Lifestyle
- Review and discuss current administrative practices surrounding the Servers.
- Review and discuss and recommend monitoring strategies around the Servers.
- Review and discuss and recommend auditing strategies of the Servers.
Maintain a Relationship with Doctors in Case of an Illness
- Good to have a relationship with an infrastructure provider, like Zunesis, when issues arise and advanced assistance is needed.
- Good to have an independent third-party, like Zunesis, doing the health checks. You aren’t allowed to prescribe your own medication, are you?
These should be included in a larger Infrastructure Monitoring Program with documented Policies and Procedures. The checks and the levels may vary depending on the organization.
Just like the human body, proper monitoring and care can assist in keeping your Servers healthy. Your Servers can only benefit from these periodic “doctor” visits. The Zunesis Infrastructure Health Check will assess your current Server Infrastructure and deliver a report providing a third-party review, validation, and recommendations for improvement. Contact Zunesis today to schedule a health check for your organization.
Growth in Hybrid Cloud
It is probably no surprise to anyone reading this that the move to Hybrid Cloud is picking up pace. IT organizations are moving data and workloads offsite for protection or to expand resource capacity more dynamically without increasing their capital spend. Of course, protection and capital management are just a couple of examples. The reasons and use cases for the growth of Hybrid Cloud are evolving nearly as fast as the technology that makes the hybrid infrastructure more viable than ever before.
As a storage focused Solution Architect, my perspective is data-centric. I look for ways to get data to the cloud most efficiently. My interests are motivated by how we use, migrate, and protect that data once it’s there. I need to answer questions about presenting the data to applications and compute resources, how to migrate it from one Cloud provider to another, and how to restore it back to on-premise resources.
Options for Managing Data in a Hybrid Environment
Management of data in a hybrid environment is facilitated by an increasing number of solutions today. This week, I’d like to highlight three cloud-based data solutions from Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE). Two of the HPE solutions I’ll be summarizing here are part of an HPE Cloud Suite. Those solutions include HPE Cloud Volumes Block and HPE Cloud Volumes Backup. The third solution has been around for some time and is not officially considered part of the Suite. However, I think it is important as a consideration in an overall Data in the Cloud strategy. That third solution is HPE Cloud Bank Storage.
The HPE Cloud Suite
As I mentioned before, the HPE Cloud Volumes Suite consists of a pair of enterprise-class, on-demand data services from HPE that provide Block and Backup storage on an HPE Cloud platform. Each of these services leverage technologies from HPE that can also be found in their on-premise solutions. Cloud Block utilizes Nimble Storage and Cloud Backup utilizes the StoreOnce Catalyst Store.
Together, these services can provide an on-premise experience. But, to be clear, you don’t need to have Nimble or StoreOnce on-premise in order to use these HPE data services. The idea behind Cloud Volumes is to provide access to your data from anywhere and allow you to move data between workloads across the major cloud providers that include Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
The HPE Cloud Volumes Suite is a pay-as-you-go service. You only pay for what you use. Because your data is on an HPE platform, you don’t need to worry about egress fees as you would with the other cloud providers. However, because the HPE platform has data locality beside the other service providers, you can present your data to compute resources located on the other platforms. This means you can move data between the other cloud services providers quickly and without additional charges. The result is the elimination of cloud provider lock-in.
So, let’s take a quick look at each of the Suite data services.
Cloud Volumes Block:
This service provides enterprise cloud-based Block storage to use for volumes that will connect to workloads running in Azure, AWS, and GCP. The storage is located on HPE’s cloud platform but with data locality near the cloud provider(s) of your choice. Because HPE Cloud Volume Block is separate from the workload platform, you can migrate data from one provider to the other without egress charges; the data doesn’t change its location, only the workloads change locations.
As mentioned earlier, HPE Cloud Volumes Block uses HPE Nimble technology and all the features you’d expect on that array platform. And, as with HPE Nimble on-premises solutions, you can expect six 9’s (99.9999%) availability with HPE Cloud Volumes Block. While the management interface is different than the on-premise Nimble Array, the ease of provisioning volumes still exists.
Using the HPE Cloud Volumes Portal, you can choose your Workload Cloud Provider, Cloud Application, Volume Type, Performance Characteristics, Size and Application Hosts to which you will present volumes. And, of course, you can specify snapshot schedules, whether to encrypt the volume, cloning, etc.
Features of HPE Cloud Volume Block include:
- Multi-cloud (AWS, Azure, GCP)
- Instant Snapshots and Clones
- 256-bit volume encryption
- Nimble replication from on-premise to Cloud
- REST API
- CLI
- Container support (Docker, Kubernetes, Mesophere)
- SoC2 Type 1-certified
- HIPAA-compliant
So, what are your workload requirements? Test/Dev? Production? HPE Cloud Volumes Block is suited for either of these use cases.
Cloud Volumes Backup:
As the name implies, this part of the HPE Cloud Volumes Suite provides a cloud-based backup target. We are all familiar with the 3-2-1 backup/recovery strategy where you maintain 3 copies of your data on 2 types of media with 1 copy off-site. HPE Cloud Volumes Backup fulfills the off-site part of that strategy.
The HPE Cloud Volumes Backup service integrates with some of today’s leading backup ISV’s, including Commvault, Veeam, and Veritas. There is also support for MicroFocus Data Protector. What this means is that you can start using Cloud Volumes Backup immediately if you already use one of these ISV backup/recovery solutions. In addition to the ISV’s mentioned, Cloud Volumes Backup integrates with HPE RMC (Recovery Manager Central) for protection directly from on-premise HPE Primera, HPE 3PAR, and HPE Nimble. But, to be clear, if you are using a supported backup/recovery software solution, you can protect data on any storage array supported by the ISV.
One of the goals for any backup/recovery strategy these days is to provide an extra layer of protection from a Ransomware attack. After all, it is reported that there is a ransomware attack happening every 40 seconds. To provide protection from ransomware, HPE Cloud Volumes Backup incorporates the HPE Catalyst protocol. This protocol creates data Stores that are not directly accessible by the OS, making the backup images invisible and inaccessible to ransomware.
With high-profile reports of data loss and increasing levels of government legislation for data security, companies are seeking to encrypt their data. With Cloud Volumes Backup, data is encrypted in-flight and at rest. Data on the wire travels under an AES-protected SSH tunnel to HPE Cloud Volumes Backup. Data at rest can be encrypted with 256-bit AES-encryption.
And, in case you were wondering, HPE Cloud Volumes Backup offers built-in multitenant security. Backup volumes created by one user are not visible to others, even if they are stored on the same device. Management or provisioning access, as well as data access, is also multitenant.
In addition to security, you are also likely concerned about being able to assure the integrity of the data you are trying to protect. The reliability of your backed-up data sets is critical. It would be a disaster to restore your data from a backup location only to find it is corrupt. HPE Cloud Volumes Backup provides data integrity throughout its lifecycle by providing built-in protection that checks data at multiple stages. Data is checked during backup, while at rest, and during recovery.
Finally, in addition to being ready in the event of a data recovery event, where you would be restoring data back to your on-premise array, HPE Cloud Volumes Backup can be used to restore data to HPE Cloud Volumes Block. It leverages public cloud compute resources for disaster recovery, test/dev, reporting, analytics, etc.
Cloud Bank:
So far, we’ve talked about cloud-based storage for production and test/dev workloads as well as storage for your off-site, standard retention backup target. An important consideration for any backup/recovery strategy is how you will manage your long-term, archive storage. To that end, HPE Cloud Bank is designed to be used as long-term archive object storage.
Cloud Bank is an extension to the HPE StoreOnce Backup Appliance. The design assumes you will store short-term retention data on an on-premise HPE StoreOnce appliance. Then, it tiers that data to HPE Cloud Bank for longer-term retention and archival data. Cloud Bank leverages a customers’ provisioned object storage in either Azure or AWS. It funnels data to and from those objects stores through StoreOnce.
In contrast, HPE Cloud Volumes backup is an as-a-service offering. A customer can have backups near to the cloud without managing a cloud infrastructure, or any on-premises appliances or licenses. You can also restore from Cloud Volumes Backup directly to any array, or, to Cloud Volumes Block, so that data can be used with GCP, AWS, or Azure compute.
Depending on your use case, all three of the cloud-based storage solutions presented here may work for you. Whatever you are looking to achieve with your cloud-based data footprint, one of these options is likely to get you there.
Contact Zunesis for more information on how to manage data in a hybrid cloud environment.