Every 11 seconds, a network is attacked by ransomware. Each successful attempt costs a company $80,000 on average. This adds up to over $20 billion each year. This number continues to grow each year. Cyber security is quickly becoming one of the most important investments for companies large and small.
These investments come in many forms; training, antivirus programs, spam filters, and backups to name a few. Once your data is compromised though, there is really only one thing you can do. You need to do a restore from a backup.
So, how does Veeam backup help protect data against ransomware?
Immutable backups
Immutable backups are copies of your data that cannot be changed. Veeam offers immutability in the capacity tier of their Scale-out Backup Repository (SOBR). It leverages a native function of object storage that prevents blocks of data from being changed for a set amount of time. Not even a malicious admin with full access to backups can change this data, let alone ransomware.
Air-Gapping
A related concept is air-gapping your backup repository. This basically means backups are unreachable or offline after the backup is taken. A common way of doing this is tape backups. Once the tape is written, it is physically removed from the network. It is stored in a secure location, inaccessible until the tape is moved back onto the network.
Another feature offered by Veeam that is similar is rotated media. This allows to swap hard drives for the backup chains so that one or more hard drives with backup data are offline or air gapped at all times. This protects that set of data from attacks.
Veeam ONE
Detecting ransomware in its initial stages can be difficult. Veeam ONE provides the ability to monitor your environment closely and be aware of any suspicious or abnormal activity. By analyzing CPU usage, datastore write rate, and network transmit rate, Veeam ONE can help identify higher than normal activity on a particular machine, trigger an alarm, and immediately notify you to inspect the machine.
Veeam SureBackup
SureBackup is a feature of Veeam that allows you to create a sandbox to test your backups before restoring them to production. It can run virus and malware scans on backup sets, automatically or manually. It ensures your data is not infected without the need to restore the data somewhere first.
Secure Restore
A related feature is Secure Restore, which scans your data as it is being restored. This gives you access to the latest virus definitions which helps safeguard against viruses that were previously unknown at the time of the backup.
Veeam DataLabs
Unsure of a workload, or suspect it may be infected? DataLabs gives you the ability to restore the data to a fully secured and isolated environment to test. A fully isolated sandbox lets you run any tests you want without impacting production systems, so you can make sure your workloads are uninfected before you restore them.
Ransomware protection alliance
Veeam is part of a group of leading hardware and software companies, like HPE, Cisco, and AWS, that work together to make sure their products integrate using the highest security standards possible. They bring together the most powerful recovery solutions to combat ransomware.
Veeam backup and recovery is a powerful tool in the fight against ransomware. It is completely dependent on how it is implemented and used. You should always secure your backup server, follow the 3-2-1 rule, implement Veeam’s features for ransomware detection, protect your network, and test your backups. A good backup strategy is just another piece in the puzzle in the fight against ransomware.
Contact Zunesis to find out more about Veeam backup and recovery solutions for your organization.
Access to your Business-Critical Data and Applications
There are many facets to a thoughtful plan for maintaining highly available access to your business-critical Data and Applications. The consideration starts with the location of your hardware infrastructure components (Compute, Networking, Storage). Does the facility provide security, cooling, reliable and redundant power, etc.? Are your hosts, storage and network equipment designed with redundancy, i.e, Power Supplies, Fans, Drives, etc.? Does your design include Clustering, Replication, perhaps a Disaster Recovery site? All of these are part of a complete plan.
But, even the most highly available hardware infrastructure is not much use without the Data and Applications it is configured to support. For protection of data and applications, we must have a Backup/Recovery process in place. Often, with Backup/Recovery implementations, the biggest effort is with the initial setup. This is where the software is installed, backup targets are configured, and backup jobs are defined. After that, the jobs get monitored periodically. If the job status is green, then nothing more is done until a file or Virtual Machine (VM) needs to be recovered.
Testing is Important
While taking time to plan the jobs and maintain consistent monitoring of them is critical, testing the Recovery of the Data and Applications being protected is equally important. All of us would likely agree we need to validate our Backup data. However, this is a step that is often pushed to the side because of competing priorities in every IT environment. For many IT environments, Backup/Recovery becomes a “set it and forget it” activity. The focus is mainly on the Backup process.
So, perhaps the answer to ensuring we validate the recoverability of what we are backing up is to automate the validation process. At Zunesis, we partner with Veeam to help our clients protect their Data and Applications with Veeam Backup and Replication (Veeam B&R). If you aren’t familiar with Veeam, let me provide a brief summary.
Veeam Backup and Replication
Veeam B&R is a Backup/Recovery application for protecting any workload, including virtual machines, physical servers, Oracle, Microsoft SQL, Exchange, Active Directory, Microsoft SharePoint, NAS, and Cloud. These don’t represent everything that Veeam B&R can protect, but this list should make it clear that Veeam will likely be able to protect any workload in your environment. Furthermore, Veeam has built-in Replication, WAN Acceleration, Integration with many storage arrays, Encryption, Deduplication, Compression, and more.
Veeam SureBackup
But the one feature I want to highlight here is Veeam SureBackup. Perhaps you use Veeam and have seen the SureBackup option in the management console but never really explored its capabilities. To summarize, SureBackup is the Veeam technology that lets you test VM backups and validate that you can recover data from them. With SureBackup, you can verify any restore point of any VM protected by Veeam B&R. Using SureBackup, Veeam B&R can boot the VM from the Backup in an isolated environment, scan VM’s for malware, run tests against the VM, power the VM off and create a report on the recovery verification results. The report can then be automatically emailed to you for review.
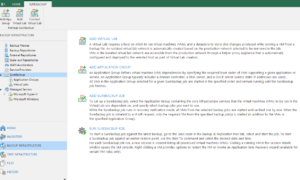
As referenced below, SureBackup is a feature you would see whenever you are viewing the Veeam B&R Management Console. And like most of the Veeam features, you are guided through its setup using a step-by-step process in the Management Console. The screenshot shown below lists the major steps (in order) for setting up the SureBackup environment.
While it is beyond the scope of this post to walk you through the entire setup, I would like to provide you a summary of the setup using the steps outlined in the screenshot above. Through this Summary, I hope to convey the power of the Veeam SureBackup feature.
It is important to remember that the SureBackup feature utilizes VM’s that are protected by scheduled Veeam Backup Jobs.
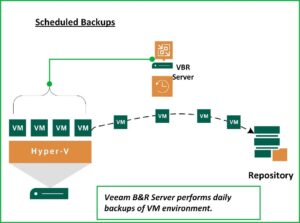
Once you have the Backup Jobs defined, you can setup the SureBackup environment to validate that what you’re backing up can be restored when the need arises. So, let’s take a look at the major steps required to implement SureBackup.
ADD VIRTUAL LAB
The first step in building a SureBackup environment is to Create a Virtual Lab. The virtual lab is an isolated virtual environment in which the backed up Virtual Machines are started and tested. You can create multiple Virtual Labs depending on your needs. During the creation of the Virtual Lab, Veeam B&R will deploy a Linux Appliance that will fence off your Production environment from the Virtual Machines being tested.
The Appliance will act as Gateway, provide DHCP, and Routing to the isolated environment while facilitating access from the Production environment if needed. To accomplish this, the Appliance has network access to both the Production environment and to the Virtual Lab. With the Appliance in place, VM’s can be restored to the virtual lab using the same IP Addressing as they have in the Production environment from which they were Backed up. The Appliance will keep any conflicts from arising between the two parallel environments.
ADD APPLICATION GROUP
With the Appliance in place, it’s time to create the Application Groups. An Application Group includes the VM’s you want to validate along with any VM’s they may be dependent upon. For instance, if you want to test a SQL Database Server, you will probably want to have a Domain Controller and DNS Server available and perhaps the Application Server. So, the Application Group is the place where you define a working environment for the workloads you want to validate.
ADD SUREBACKUP JOB
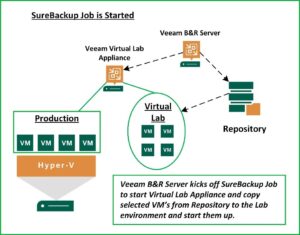
With the Virtual Lab(s) and Application Group(s) Defined, it’s time to create the actual SureBackup Job that will build the environment on-demand or based on a schedule. In this step you will specify the Virtual Lab you’ll be using and the Application Group you’ll be including in that Virtual Lab. Then, you can select from the Backup jobs you already have running to specify the VM’s you’ll want to validate.
As part of the Job creation you can configure what you want to test/validate for each VM. Examples of validation criteria include testing the disk content for corruption, scanning VM’s for malware, and performing PING tests. During the setup you are able to select predefined test scripts or include custom scripts to use for testing. Once all the components have been defined, you can schedule when you want the jobs to run (Daily, Weekly, Monthly). You will also decide to whom the Job results should be sent.
Benefits Worth the Effort
So, as you can see, the SureBackup environment will take a little time and planning to build and test. The benefits are well worth the effort.
It provides an automated method of validating Backups. Its design allows for the Virtual Lab to be created on-demand. This is an environment where one can test server and software updates, perform security testing, and conduct DevOps and Analytics. This is all done without impacting your Production environment. Veeam calls this capability the On-Demand Sandbox.
If you already use Veeam B&R, but haven’t tried the SureBackup option yet, I hope this post has encouraged you to give it a try. If you do not currently use Veeam, I hope your interest is peaked and you want to learn more. In either case, Zunesis has Solution Architects who can help you. We have Veeam B&R deployed in our lab so you can explore for yourself the SureBackup functionality. You can get a better understanding of this important piece of a thoughtful plan to maintain highly available access to your business-critical Data and Applications.
As we approach day [xyz] of the plague, I was ready to write another blog post about COVID-19 and technology. It seems that all we can think about lately is the virus. Working from home with three kids under 10 years old certainly has been “fun” for me. I’ll definitely be glad once this thing is gone.
Ransomware Uptick
Instead, I’d like to take some time to talk about ransomware. Another currently rampant plague of the digital variety. Among malware, ransomware is some of the absolute worst of the worst. It certainly has it’s own place in H-E double hockey sticks.
At a time where people and businesses are already suffering, we are seeing an uptick in ransomware attacks. Encryption of your files occurs, and cyber criminals demand a ransom in order to decrypt them. Often times, organizations use military grade encryption. So, the only way to decrypt the files is to pay the ransom.
Since only the criminals have the required decryption keys, it would be nearly impossible to decrypt even with your handy dandy cereal box decoder ring. Unfortunately, paying the ransom is a risky proposition. There is no guarantee that your files will be decrypted. This also validates the cyber criminal business model and encourages bad actors.
Ransomware spreads like fire, and burns the building to the ground if you don’t prepare.
How to deal with ransomware
BACKUP
First of all, you REALLY should have good backups. This doesn’t prevent the ransomware attack, but it certainly prevents you from needing to either a)open up your wallet or b)lose important data.
You might be surprised how many of us don’t follow rule #1 for data. Backups should be available locally, as well as off-site/cloud. You should also make sure that you can restore multiple points in time. This is in case your more recent backups contain ransomware. This isn’t just best practice for ransomware, it is just good practice in general.
Whether it comes in the form of ransomware, hard drive failure, data corruption, or space aliens shooting lasers at your PC, you really should have a plan for your data. How much is your data worth to you? For the ransomware event, skip the heartburn and restore from backup prior to an attack.
Prevent ransomware with good personal cyber hygiene
Be proactive with cyber security. Here are some suggestions:
- Rule #1 – Take regular backups
- Rule #2 – Take regular backups
- Rule #3 – Make sure your backups are good, and validate that you can restore from them.
- THINK BEFORE YOU CLICK
- Make sure that you are using reputable antivirus and malware protection to stop most threats.
- Stop believing that your AV/Malware prevention suite will stop 100% of attacks, zero day exploits will keep coming.
- Do not open files from people that you do not know, or click on random email links from your “bank” asking you to “update” your information.
- Have a good firewall, network segmentation, SPAM filter, etc.
- Don’t re-use the same few passwords for EVERYTHING. Do not use the same password with 1,2,3,etc., to get around password complexity requirements not allowing you to re-use your password.
- Use multi factor authentication where possible.
- Make sure that you are updating your operating system regularly.
- Security patches don’t work if you don’t install them.
What to do if you get hit with Ransomware
Hopefully this will always be theoretical, and you never get hit. First of all, you definitely want to isolate the machine. This stuff will scan your ARP tables, your registry, and a variety of other sources to look for other hosts to infect. I’d say immediately power off, enter the nuclear codes, and kill it with fire. In other words, wipe/erase the machine. You can then move forward with rebuilding the OS and restoring your data once you’ve got a blank canvas. Just because your security scan came up clean does not 100% guarantee a malware free result.
Next, if there are other machines on the network, quarantine and examine them. Ransomware will proactively work to infect everything else it can on the network. If other machines are impacted, they should also be nuked and rebuilt. This includes your business critical servers. Actually, this is especially critical for business critical systems. These systems house critical data, and are often a central point of access(points of infection) by many users. YES, THIS IS PAINFUL. However, if you have good backups to restore from, it isn’t nearly as big of a deal.
Are you prepared?
Much like the human pandemic that we are all too familiar with, hopefully you are “distancing” yourself from the digital pandemic. The best way to beat a ransomware attack is prevention, not reaction after the fact when it’s too late. If you need help preparing, or even just a second set of eyes to review your existing strategy, please contact us for an assessment. We are here to help.
What? You still aren’t backing up your Office 365 Tenant?
Office 365 has become one of the most popular cloud-based productivity platforms. According to a recent study performed by Barracuda, “Market Analysis: Closing Backup Recovery Gaps”, more than 60% of IT professionals are using it to drive business success in some fashion. Email is the most popular (78%), followed by OneDrive (60%), SharePoint (50%), Teams (36%), and OneNote (35%).
Office 365 Security
Microsoft has done a good job in creating “Best Practices” for Office 365 Tenant Security. On January 6, 2020, they released the “Top 10 ways to secure Office 365 and Microsoft 365 Business Plans.” Its aim is to help secure organizations achieve the goals described in the Harvard Kennedy School Cybersecurity Campaign Handbook.
Microsoft recommends the following be applied to your Office 365 environment:
- Setup multi-factor authentication
- This is the easiest and most effective way to increase the security of your organization. Add a 2-step verification to all accounts. In addition to the password, there is a second component. This is usually a mobile device, which provides a code received from Office 365.
- Train your users
- Establish a strong culture of security awareness within the organization. This includes training users to identify phishing attacks. For example, don’t open the attachment just because someone you know sent it to you.
- Use separate/dedicated admin accounts
- Admin accounts are valuable targets for hackers. Admins should have a separate account for regular, non-administrative use.
- Raise the level of protection against malware in email
- Blocking of attachments with file types that are commonly used for malware.
- Protect against ransomware
- Warn users of messages originating external to the organization. Blocking of file extensions that are commonly used for ransomware. Warn users who receive attachments that include macros.
- Stop auto-forwarding for email
- Hackers who gain access to a user’s mailbox can exfiltrate mail by configuring the mailbox to automatically forward email.
- Use Office 365 Message Encryption
- Organizations can send and receive encrypted email messages between people inside and outside the organization.
- Protect your email from phishing attacks
- Configure anti-phishing protection, ATP (Advanced Threat Protection). This can help protect from malicious impersonation-based phishing attacks.
- Protect against malicious attachments and files with ATP (Advanced Threat Protection) Safe Attachments
- Helps determine whether an attachment is safe or malicious.
- Protect against phishing attacks with ATP (Advanced Threat Protection) Safe Links
- Hackers sometimes hide malicious websites in links in email or other files. Safe Links can help protect by providing time-of-click verification of web addresses (URLs) in email messages and Office documents.
Where’s Backup
 One glaring omission, not purposely according to Microsoft, is backup and retention of Microsoft 365 data. Microsoft does not hide the fact that they do not backup or provide long-term retention of Microsoft 365 data.
One glaring omission, not purposely according to Microsoft, is backup and retention of Microsoft 365 data. Microsoft does not hide the fact that they do not backup or provide long-term retention of Microsoft 365 data.
Wait……. What?
That’s right, Microsoft does not provide backup or long-term retention of Microsoft 365 data.
Let that sink in.
Microsoft does not provide backup or long-term retention of Microsoft 365 data.
An estimated 40%, that’s right 40%, of Microsoft 365 organizations aren’t using any third-party backup tools to protect their mission-critical data. Mostly due to a major misconception that Microsoft is backing up their data for them.
40% of Microsoft 365 Organizations
are not using third-party backup tools to protect
their mission critical data
Microsoft uses the term, shared responsibility model:
- They have physical security in their data centers.
- They offer data storage replication and redundancy.
- Their SLAs include guarantees of uptime and privacy controls.
- They will protect you from natural disasters that affect their data centers, hardware or software failures on their part, power outages, operating system errors, etc.
- You are responsible to protect your data from human error (due to malicious activity or innocuous accidents), misconfigured workflows, hackers, and viruses. Backing up your users and data is truly your responsibility. If you are not proactive about that, any help you get from Microsoft in times of crisis is minimal at best.
In other words, while Microsoft provides a resilient SaaS infrastructure to ensure availability, it does not protect data for historical restoration for long. Its SLAs don’t protect against user error, malicious intent or other data-destroying activity. In fact, deleted emails are not backed up in the traditional sense. They are kept in the Recycle Bin for a maximum of 93 days before they’re deleted forever. If a user deletes an email, and the retention period is reached, that email is gone forever. If a user deletes their whole mailbox, the admin doesn’t realize, and the retention period is reached, the whole mailbox is gone.
On SharePoint and OneDrive, deleted information is retained for a maximum of 14 days by Microsoft. Individuals must open a support ticket to retrieve it. SharePoint and OneDrive are unable to retrieve single items or files. They must restore an entire instance. It’s unlikely that such short retention policies will meet most compliance requirements.
Don’t Make a Costly Mistake
Many assume that Microsoft will support their backup requirements for Office 365 data. This could be a costly mistake. If they suffer a serious incident, they could find that crucial data has been deleted permanently. There are plenty of advanced, cost-effective third-party backup and recovery solutions for Office 365. IT Managers should revisit their backup strategies to ensure there are no gaps in coverage, especially in cloud-based applications, such as Office 365.
Need assistance navigating Microsoft products and backup solutions, contact Zunesis.
Ransomware
In May 2017, the National Health Service of England and Scotland was hit with the largest ransomware attack at that time. The attack affected an estimated 200,000 computers across 150 countries. The estimated economic loss ranges from hundreds of millions to four billion dollars. This attack, dubbed the WannaCry ransomware attack, catapulted network security to the top of many organization’s priority list. It brought to light the amount of damage that could be done by a malicious virus.
What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is a type of malicious software, or malware. It is designed to deny access to a computer system or its data until a ransom is paid. It is typically spread through phishing emails or by visiting an infected website. The virus works by encrypting all the data on the user’s hard drive. Then, it requests a payment, usually in the form of cryptocurrency, to be sent to the hackers. However, there is no guarantee the user will recover their files if they pay that ransom.
Ransomware can be devastating for users and organizations. Currently, we are seeing a lot of government agencies, education organizations, and healthcare organizations targeted by these attacks.
What precautions can you take?
In order to protect your user’s and organization’s data, there are a number of precautions you can take. Most of which are best practice even without the threat of ransomware.
First, keep all applications and operating systems up to date. Outdated apps and OS’s are the target of most attacks. This was the case in the WannaCry attack.
Second, train users to avoid phishing emails. These are emails designed to look legitimate at first glance but have links that redirect you to an infected site, or attachments that download the malware directly. Phishing emails and sites are also associated with social engineering attacks designed to steal credentials. It is always a good idea to train users to never click on links or open attachments in unsolicited emails.
Next, backup your data on a regular basis. Backing up your data is a good idea for a myriad of reasons. It can really save you in the case of a ransomware attack. Best practice would be to keep 3 copies of your backups, with one offline and another in a geologically separate location. These backups should also be regularly tested.
A great way to control what is installed on your organization’s computers is access control. Restricting privileges may not allow malware to be installed on a system without an administrator’s approval. This will limit the spread of the malware through a network.
Similarly, another useful tool for fighting malware is a spam filter on your emails. A strong spam filter will prevent most phishing emails from making it to users’ inboxes. It will authenticate inbound emails to prevent spoofing.
What to do when you’ve been infected by ransomware
The first thing anyone should do when infected by ransomware is to contact law enforcement immediately. You should report the infection to the FBI’s cyber task forces and internet crime complaint center.
Currently, the FBI does not recommend paying any ransom. While it could cost organizations large sums of money to be down for any length of time, there is no guarantee that paying the ransom will restore your data. There are numerous cases of this happening. Some victims who have paid the ransom have even been targeted again. Other victims have even been asked to pay more after the original ransom to get all their data back. Paying may inadvertently encourage this criminal business model. This makes it more prevalent in the future.
Once you have found out that you are infected, you should isolate any infected machines immediately. In addition, one should take any unaffected machines offline so they don’t get infected. Same goes for backups. They should be taken offline immediately to stop the ransomware from spreading into your backups.
From there, you should follow your organization’s incident response plan. Follow any instruction given to you by law enforcement.
There will never be any way that you can guarantee you won’t fall victim to one of these attacks. Malware is always evolving, just like security practices are. It will always be an arms race between hackers and security experts. Your best bet is to always follow best security practices, and to always have a plan to recover from any successful attacks.
Where to report Activity
FBI
Internet Crime Complaint Center
United States Secret Service
Contact Zunesis to have an assessment done on your current infrastructure. Ask us about helpful hints to help keep your data secure.
Do you have control of your Office 365 data? Do you have access to all the items you need?
The typical reaction is, “Microsoft takes care of it all.”
Microsoft takes care of quite a bit and provides a great service for their customers. However, Microsoft’s primary focus is on managing the Office 365 infrastructure and maintaining uptime to users. They are empowering YOU with the responsibility of your data. The misconception that Microsoft fully backs up your data on your behalf is quite common, and without a shift in mindset, could have damaging repercussions when this responsibility is left unattended. Ultimately, you need to ensure you have access to, and control over, your Exchange Online, SharePoint Online and OneDrive for Business data.
The misunderstanding falls between Microsoft’s perceived responsibility and the user’s actual responsibility of protection and long-term retention of their Office 365 data. The backup and recoverability that Microsoft provides and what users assume they are getting are often different. Meaning, aside from the standard precautions Office 365 has in place, you may need to re-assess the level of control you have of your data and how much access you truly have to it.
As a robust and highly capable Software as a Service (SaaS) platform, Microsoft Office 365 fits the needs of many organizations perfectly. Office 365 provides application Availability and uptime to ensure users never skip a beat, but an Office 365 backup can protect you against many other security threats.
6 reasons why backing up
Office 365 is critical
1. Accidental Deletion
If you delete a user, whether you meant to or not, that deletion is replicated across the network, along with the deletion of their personal SharePoint site and their OneDrive data. Native recycle bins and version histories included in Office 365 can only protect you from data loss in a limited way, which can turn a simple recovery from a proper backup into a big problem after Office 365 has geo-redundantly deleted the data forever, or it has fallen out of the retention period.
There are two types of deletions in the Office 365 platform, soft delete and hard delete. An example of soft delete is emptying the Deleted Items folder. It is also referred to as “Permanently Deleted.” In this case, permanent is not completely permanent, as the item can still be found in the Recoverable Items mailbox. A hard delete is when an item is tagged to be purged from the mailbox database completely. Once this happens, it is unrecoverable, period.
2. Retention Policy Gaps and Confusion
The fast pace of business in the digital age lends itself to continuously evolving policies, including retention policies that are difficult to keep up with, let alone manage. Just like hard and soft delete, Office 365 has limited backup and retention policies that can only fend off situational data loss and is not intended to be an all-encompassing backup solution.
Another type of recovery, a point-in-time restoration of mailbox items, is not in scope with Microsoft. In the case of a catastrophic issue, a backup solution can provide the ability to roll back to a previous point-in-time prior to this issue and saving the day.
With an Office 365 backup solution, there are no retention policy gaps or restore inflexibility. Short term backups or long-term archives, granular or point-in-time restores, everything is at your fingertips making data recovery fast, easy and reliable.
3. Internal Security Threats
The idea of a security threat suggests hackers and viruses. However, businesses experience threats from the inside, and they are happening more often than you think. Organizations fall victim to threats posed by their very own employees, both intentionally and unintentionally.
Access to files and contacts changes so quickly, it can be hard to keep an eye on those in which you’ve installed the most trust. Microsoft has no way of knowing the difference between a regular user and a terminated employee attempting to delete critical company data before they depart. In addition, some users unknowingly create serious threats by downloading infected files or accidentally leaking usernames and passwords to sites they thought they could trust.
Another example is evidence tampering. Imagine an employee strategically deleting incriminating emails or files — keeping these objects out of the reach of the legal, compliance or HR departments.
4. External Security Threats
Malware and viruses, like ransomware, have done serious damage to organizations across the globe. Not only is company reputation at risk, but the privacy and security of internal and customer data as well.
External threats can sneak in through emails and attachments, and it isn’t always enough to educate users on what to look out for — especially when the infected messages seem so compelling. Exchange Online’s limited backup/recovery functions are inadequate to handle serious attacks. Regular backups will help ensure a separate copy of your data is uninfected and that you can recover quickly.
5. Legal and Compliance Requirements
Sometimes you need to unexpectedly retrieve emails, files or other types of data amid legal action. Microsoft has built in a couple safety nets, (Litigation Hold) but again, these are not a robust backup solution capable of keeping your company out of legal trouble. For example, if you accidentally delete a user, their on-hold mailbox, personal SharePoint site and OneDrive account is also deleted.
Legal requirements, compliance requirements and access regulations vary between industries and countries, but fines, penalties and legal disputes are three things you want to avoid.
6. Managing Hybrid Email Deployments and Migrations to Office 365
Organizations that adopt Office 365 typically need a window of time to serve as a transition window between on-premises Exchange and Office 365 Exchange Online. Some even leave a small portion of their legacy system in place to have added flexibility and additional control. These hybrid email deployments are common yet pose additional management challenges.
The right Office 365 backup solution should be able to handle hybrid email deployments, and treat exchange data the same, making the source location irrelevant.
Conclusion
Whether you are considering moving your organization to Microsoft Office 365 or have already embraced the benefits of Office 365 within your organization, find a backup solution that offers you both complete access and complete control of your Office 365 data and avoid the unnecessary risks of data loss.
Data Loss is Increasing and It’s Costly
In today’s digitally active world, small businesses cannot afford to lose their data even for a short amount of time. According to research by Security Week, the total volume of data loss at an enterprise level has increased more than 400% over the past couple years. IT Web suggests that the total cost of data breaches will be more than $2.1 trillion by 2019.
A recent Verizon report found that small data breaches- those with fewer than 100 files — cost a company between $18,120 and $35, 730. Another scary statistic is that more than 90% of companies that experience at least seven days of data center down time will typically go out of business within one year.
Whether the loss of data is due to natural disaster, human error, a cyber attack or hardware failure, data loss is very risky and very expensive. That’s why now more than ever, companies need to invest time and money in a backup and discovery recovery solution to help give peace of mind and minimize costs.
Smaller businesses are actually exposed to a great amount of risk since cyber criminals know they are easy targets since many of them do not take the time or have the internal resources to guard against it. A few days of downtime for a small business can be detrimental to a business surviving.
Here are just a few more stats pulled from an article on LinkedIn in 2016 on how data loss and business continuity in the wake of disasters are highly applicable to both single location businesses storing data onsite and multi-location businesses storing data in a single cloud.
- 86% of server workloads are forecast to be virtualized by 2016 (2014-15 Virtual Server Backup Software Buyer Guide)
- The number one IT priority for mid-market organizations over the next 12 months is to improve data backup and recovery. (ESG Lab Review: Data Protection, Recovery and Business Continuity with SIRIS 2 from Datto)
- 96% of all business workstations are not being backed up (Contingency Planning and Strategic Research Corporation)
- 58% of downtime incidents are caused by human error alone. Natural disaster account for only 10% of downtime(Enterprise and the Cost of Downtime, Independent Oracle User Group, 2012)
- 35% of servers have a downtime tolerance of 15 minutes or less (ESG Research: BC/DR Survey Final Results, Enterprise Strategy Group, 2015)
- The leading cause of incidents and outages is hardware failure/server room failures. Next is environmental disasters, and last is miscellaneous outages (The 2015 Disaster Recovery & Business Continuity Survey)
- 93% of companies that lost their data center for 10 days or more during a disaster, filed for bankruptcy within one year of the disaster (National Archives & Records Administration in Washington)
- Of companies that suffer catastrophic data loss: 43% never reopen and 51% close within two years (University of Texas)
- 30% of all businesses that have a major fire go out of business within a year and 70% fail within five years (Boston Computing Network, Data Loss Statistics)
- The average cost of downtime per hour is $25,000 to $50,000+ (Advertorial Infographic: Why Disaster Recovery in the Cloud Should Be in Your Plans, International Data Group, 2015)
- Companies with 100 – 2,000 employees are likely to experience costs over $20,000 in the event of a disaster(The 2015 Disaster Recovery & Business Continuity Survey)
As we finish up 2017 and head into 2018, if your small business does not have a backup and disaster recovery solution and/or plan, it is a most have resolution for your business.
What is Backup and Disaster Recovery?
Backup and Disaster Recovery or (BDR) can be defined simply as the combination of data backup and disaster recovery solutions that are designed to work together to ensure uptime, diminish data loss, and maximize productivity in the midst of an attack, natural disaster or other compromising situation.
 Five Reasons Why Small Businesses Need a BDR Plan
Five Reasons Why Small Businesses Need a BDR Plan
- Natural Disasters: This year, the United States has been hit by several natural disasters from floods to fires, earthquakes, and more which are uncontrollable circumstances which caused many businesses to experience downtime. Is your small business prepared when natural disaster strikes?
- Cyber Attacks: Cyber criminals are focusing more of their attention on businesses they feel are unprotected which makes small businesses more vulnerable. A BDR plan can limit the impact of an attack and hopefully prevent the business from losing valuable data.
- Protect Client Data: Are you a retailer or online business where you are housing client data? A BDR plan will help ensure that their information is properly stores and controlled. A security breach could ruin the reputation of your brand and business and the future of your business.
- To Err is Human: Sometimes the employees of a business can be at fault for data losses. Not only is it important to train a company’s staff properly but also have backup solutions that are available in case situations like this arise.
- Systems Can Fail: No solution is every perfect. Hardware, machines and other systems can fail. Even systems that come with 99.95 uptime guarantees may falter every once in a while.
Putting Together a Plan and Checklist
You know that you need a disaster recovery plan but do not know where to start. First, make a list of all the technologies your business uses. Then, go through each department in your company and determine what technology that department needs to function on a day-to-day basis. How long realistically can your business be down and still operational?
Identify which items in your business need the most protection. You may not need to backup your entire systems. Create a list detailing crucial data and examine their location. This information will allow you to make decisions on the frequency of backups and how much storage you may need.
Create a Schedule for your Backup and determine your storage needs. Depending on the industry of your business, you may not need to retain every backup created unless there are legal requirements which may require different regulations such as companies in the healthcare and financial industries.
What to look for in a BDR Solution?
How does a company pick the appropriate BDR solution that fits for their business? There are a few things to consider: Hardware Compatability, Scalable pricing, around-the clock support and a strong reputation. A company should do their research to find the right fit for their needs.
Zerto, one of Zunesis’ preferred partners has come up with a guide that has 10 questions that you should ask before choosing a DR solution. Download it here.
TEST TEST TEST
After implementing a backup system, it is important to routinely test your backup system. Periodically test to restore some data and be sure you can still use it. Many managed backup solutions will include test restores as part of the service.
Adjust your backup and recovery strategy as the needs of your company changes. Know what you need and how often it changes to create a strategy that protects core functions without dramatically increasing costs.
Contact Zunesis for a review of your backup and data recovery infrastructure and we can give recommendations on what will work best for the needs of your company and how to implement those solutions.
The Threats are Many and so are the Protection Methods
In a modern society, the need for cyber security touches a surprisingly large portion of our day-to-day lives. Because of the Internet of Things (IoT), we can scarcely climb out of bed each morning before we use a device that is connected to the internet in some way. Whether it’s our smart phones, Alexa, Siri, tablets, laptops, television or even our automobiles, we are potentially putting personal data out on the internet before we’ve even had our first cup of coffee (or even as we order our coffee for pickup as we head into work). We pay our bills online, we use our phones to deposit checks and we even have wi-fi enabled automobiles.
As individuals, we are responsible for looking out for our own security. As IT Professionals, we are responsible for protecting the data our company produces and collects. In many cases, the data we are protecting in our professional role is personal data, possibly our own. But, the recent Equifax breach is a harsh reminder that, even companies we associate with security are vulnerable. If there is any lesson we can take away from our personal experiences, and the stories behind the headlines, it’s that there is not single solution that will protect us from the threat of our data ending up at the mercy of people with bad intentions. Those of you reading this post are intimately familiar with the steps needed to protect company data. From the network to the desktop, and all points in between, there are many layers to a data protection strategy. One such layer is the Data Backup solutions we use.
Backup, the Original Data Protection
Decades ago, during simpler times, data protection meant being diligent about performing regular backups of data in case a file was accidentally deleted, corrupted or the hard drive crashed. Back in that simpler time, the media to which businesses directed those backups was almost always Tape, lots of tape! This process typically included keeping a set of tapes onsite for immediate restore needs and sending a second set offsite in case of catastrophe and for longer term retention. However, over time, Tape has been increasingly replaced by disk-based backup targets (think HPE StoreOnce, Data Domain, ExaGrid).

Disk-based backup targets started out as a faster way to get data backed up. Tape was still used but typically as a secondary backup target and for longer term retention offsite. The need to go to an offsite backup for file recovery was rare and so tape became that insurance policy that was never going to be needed. As use of disk-based backups became more prevalent, the technology employed to store data evolved. Improvements in compression, deduplication, and replication improved the efficiency of storing larger amounts of data (in the petabytes) and replicating that data to offsite facilities. In fact, with the ability to replicate data from one disk-based target to another over distance, we have started to see Tape being replaced at offsite facilities as well.
Backups As Our Last Defense
While we originally used backup for recovery from accidentally deleted files, random corruption and the occasional disk crash, the world we live in today requires a broader definition for Data Backup. Today, we may need to leverage our backups to recover from a Cyberattack that has either corrupted our data or rendered it unusable as part of a Ransomware attack. Because these kinds of attacks target files on volumes that are persistently mounted to hosts, the vulnerability of disk-based backup targets has come under some scrutiny lately.
Of course, many question whether the risk to disk-based backup targets is very high. After all, backup environments are typically isolated from other, more accessible, areas of the IT infrastructure. Moreover, because of the potential for Cyberattacks on the disk-based backup targets, other processes have been documented and are being implemented to mitigate the risk further. We are starting to see some of these added protections built into the backup software we use and many manufacturers of the disk-based backup devices are providing their own best-practice processes.
Despite the fear of risk for disk-based solutions, we aren’t seeing a trend away from disk-based backup, but we are hearing reports that some companies are once again turning to Tape as their last form of defense against the type of Cyberattacks that would corrupt, delete or encrypt their data. And while disk-based technology has been evolving, tape technology has also continued to evolve. LTO7 technologies provide capacities as high as 15TB (compressed) per tape cartridge. In addition to high capacities and a low TCO, Tape offers encryption at-rest, can be kept offsite and most importantly offline.
So, as we implement safeguards to keep the bad guys out of our IT infrastructure, we need to remember that our plans should include multiple layers. We also need to prepare for the possibility that our best efforts will be thwarted and that our data will be compromised. So, as part of our protection against malicious behavior and risk to our data, we need to carefully plan our Backup processes by taking the layered approach as well.
Have you heard about Zerto? More importantly, are you using Zerto?
Zerto is taking the IT world by storm, providing a simple, yet fully functional, replication and data protection Disaster Recovery (DR) solution.
What makes Zerto so unique is its simplicity.
Zerto Virtual Replication 4.5 was recently released, and this blog provides a description of some of the additional functionality provided in 4.5. (If you would like to learn more about Zerto aside from the newest features released in 4.5, please reach out to Zunesis.)
Zerto Virtual Replication 4.5 builds upon their always-on replication, with no snapshots, replication and orchestration capabilities by adding granular recovery. Now, a single file or folder can be recovered from the journal, improving the average time to recovery for files, folders, VMs, applications, and sites.

Many other improvements were made to simplify disaster recovery operations, further reducing ongoing management and maintenance, and to automate more DR operations to ensure consistency and repeatability.
File and Folder Recovery from the Journal – What is the most common disaster that administrators must recover? It isn’t natural disasters or site outages; it is actually lost or accidently deleted files or folders. In release 4.5, Zerto solves this most frequent disaster problem by adding the ability to recover a single file or folder from up to 14 days in the past, from increments in seconds from the journal with just a few mouse clicks. With other solutions, the file is pulled from nightly infrequent backups, which could result in data loss and missed user expectations.
Improved Role-Based Access Control – The security of your business continuity and disaster recovery plan is of the utmost importance. It is imperative that those who are making changes or updates fully understand the impact of these changes in the event that recovery is needed. In addition to the already robust permissions available from Zerto Virtual Replication, these have been added.
View Only – The ability to log into Zerto Virtual Replication and view the settings and configurations of the BC/DR processes. This permission level does not allow for changes to be made.
Manage Workload Protection – The ability to modify virtual protection group (VPG) settings and update BC/DR plans and processes.
Recover and Migrate Workloads – The ability to actually execute the BC/DR or migration plan. Workloads will move according to the execution plan.

With 4.5, Zerto introduced new APIs to further automate VPG creation, protecting VMs and simplifying BC/DR operations:
- Simplify management with the ability to upgrade, install, uninstall, and configure Zerto Virtual Replication Appliances
- Effectively monitor alerts with all the active alerts provided with the ability to dismiss/retain alerts
- Fully automate the creation and editing of VPGs including VMs, networks, volumes, and NIC configuration to reduce install and ongoing maintenance
- Respond to changing business requirements with the ability to add and remove VMs from or to a VPG
- Increase storage efficiency with compression on the journal
- Extend the history of an application with less storage used.
In summary, Zerto Virtual Replication 4.5 ensures the continuous protection of applications, VMs, folders, and files. This increased granularity gives organizations unprecedented control over recovery operations. New APIs and role-based controls ensure the right commands are accessed and executed, further increasing control of critical IT operations.
To learn more about Zerto or to see a technical demonstration, please contact Zunesis at info@zunesis.com.

