Storage Replication
High Availability
High availability has been a staple feature in datacenters for years. Keeping the infrastructure running and the lights on is imperative for companies in a world where small amounts of downtime can result in massive losses. As a company’s data becomes more valuable, it becomes even more important to extend that high availability to include their storage.
Storage-Based Replication
This is where storage-based replication comes in. Immediate access to data becomes crucial in case of a failure at the primary location.
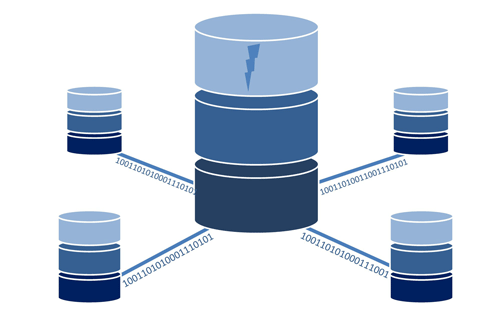
Replication is an approach to high availability that stores data in multiple locations. Data is immediately replicated to those multiple sites whenever a change is made or data is added. This allows you to retrieve that data from any of the sites. These sites could be physical datacenters owned by the organization, or geographically separate cloud instances like Azure or AWS.
Since data is immediately replicated to secondary storage as it is written to primary storage, losses can be minimized to seconds, or even eliminated completely should the primary site go down. Generally, this is controlled by software, but more and more storage arrays are being built with integrated replication making it more efficient and easier to set up.
Typically, integrated replication requires storage arrays to be either connected physically, or in a storage area network or SAN. The arrays need the ability to talk to each other at all times in order to send data to the other array as soon as it is written on the first. These replication times tend to be measured in milliseconds.
HPE Alletra’s Peer Persistence
HPE Alletra’s peer persistence is a great example of storage-based replication. Two Alletra arrays that exist on the same subnet can become replication partners. With response times under 5 ms, the arrays can get any data written to one array copied over to the other almost instantaneously. Add in some extra features like load balancing between storage pools and a 99.9999% uptime, companies can be sure their data is always safe.
Another way of setting up replication is to use software. There are many vendors, and even windows server can be used. This type of replication usually involves clustering hardware together to make identical environments that mirror each other and can be used interchangeably.
How is this Different from Backups?
So how does this differ from backups? A backup is a copy of data from a certain point in time. Replication is copied immediately. Any change to primary data is immediately replicated and no restore points are created. Backups create and store restore points from multiple times allowing you to recover from past data sets if needed.
Backups are critical in the event of corrupted or lost data. So, if a hacker encrypts your data, or an employee deletes files, you can recover all that from a previous point in time. You can’t rely on replication for data recovery. This is because any encryption or deletion is immediately replicated, making your second copy useless.
Both are critical to ensuring access to a company’s data at all times. As data is becoming more and more valuable to data-driven companies, so are the technologies used to safeguard that data.
Contact Zunesis to learn more about data storage protection offerings.
Categories
Search
Blog Categories
Related Resources
Archives
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- January 2024
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- October 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- July 2015
- June 2015
- May 2015
- April 2015
- March 2015
- February 2015
- January 2014
- February 2013